Known as the smallest gaskets, O-rings are donut-like, round gaskets that seal off space between both static and moving parts. Their goal is to prevent leaks and create a strong seal between two joined parts. O-rings are fairly inexpensive to manufacture and quite effective, making them very popular in a variety of applications. Read More…
Since 1989, we have been an o-ring distributor. We offer commercial, FDA, military, metric o-rings, caps, plugs, gaskets & more. Custom, rubber o-rings, metal o-rings, diaphragms, face seals and non-standard o-rings are also offered.

At Global O-Ring and Seal, LLC, we are dedicated to quality assurance, continually investing in rigorous product testing and validation processes to guarantee the reliability and performance our customers expect. Our goal is simple yet vital—to ensure that each sealing solution we provide is precision-engineered, durable, and perfectly suited to the demands of your applications.
RD Rubber Technology Corp is an ISO 9001:2015 / AS9100:2016 certified and ITAR registered company. We offer compression, transfer, injection and Liquid Injection molding, rubber to metal bonding, engineering support, tooling design, machining and more. Our customers rely on us to give them the best possible production o-rings. From aerospace to medical, food processing to military applications we ...
We manufacture custom o-rings at no tooling charge and no minimum order requirement. Since 1983, we have lead in sealing products with a complete range of o-ring seals, oil seals, o-ring kits, o-ring cord, hollow o-rings and metal bonded o-ring products. ISO 9002 certified with 24-hour service.

At Wyatt Seal, we specialize in delivering reliable sealing solutions, with a strong focus on high-performance O-rings. We pride ourselves on being more than just a distributor—we're problem solvers, collaborators, and partners to a wide range of industries that depend on consistent, leak-proof performance. Our selection of O-rings includes a vast array of materials, sizes, and profiles to suit ...

At American Rubber Corporation, we take pride in delivering precision-engineered rubber products that meet the highest standards of quality and performance. Our expertise in manufacturing O-rings has established us as a trusted partner across industries where durability, accuracy, and reliability are critical.

More O-Ring Manufacturers
O-rings are indispensable sealing solutions used to control pneumatic, hydraulic, and vacuum flows in a vast array of industrial and commercial applications. Their versatility is evidenced by their presence in rotating pump shafts, hydraulic cylinder pistons, gas caps, water bottle lids, engine turbines, brake systems, and countless other assemblies. O-ring seals play a critical role across numerous industries, including but not limited to: medical devices, aerospace and aviation, automotive manufacturing, chemical processing, petrochemicals and oil & gas, water treatment, food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, and even jewelry making. Their reliability and performance are essential for ensuring the integrity and safety of sensitive equipment and processes where leakage or contamination could lead to costly downtime or catastrophic failure.
The History of O-Rings
The story of the O-ring begins on May 12, 1896, in Sweden, where J.O. Lundberg was granted the first O-ring patent. However, it wasn’t until 1936 that this innovative sealing concept made its way to the United States. Niels Christensen, a Danish-American inventor, secured the U.S. patent and began commercializing the product. Despite his efforts, Christensen’s rights were largely overlooked by major corporations, who freely shared the design until Westinghouse eventually acquired control. With the advent of World War II, the U.S. government seized the O-ring patent to support the war effort—distributing manufacturing rights to a range of organizations to rapidly produce rubber seals for critical military aircraft hydraulics. Christensen later received compensation, but only after protracted legal disputes, with an initial $75,000 payout followed by an additional $100,000 for his heirs in 1971.
As O-rings gained traction, engineers quickly recognized their value and incorporated them into designs for industrial hydraulic systems, automotive assemblies, and agricultural machinery throughout the mid-20th century. The period from the 1950s to the 1970s saw remarkable advancements in synthetic rubber and polymer development, which dramatically expanded the range of materials available for producing O-rings—enabling greater application versatility and performance reliability. Today, O-ring manufacturing remains a cornerstone process in the sealing industry, with ongoing innovation in both materials and production methods.
However, the importance of rigorous quality control became tragically clear with the 1986 Challenger disaster. When a defective O-ring failed to seal the solid rocket boosters on a cold morning, it resulted in catastrophic seal failure and the loss of seven astronauts. This incident highlighted the critical need for O-rings with robust temperature resistance and the dangers of subpar quality or improper material selection in mission-critical environments.
Following this disaster, O-ring engineers and manufacturers intensified their focus on material science and quality assurance. Emphasis was placed on manufacturing O-rings with proven temperature resilience and establishing stringent standards for quality control, packaging, labeling, and shelf life. Inspection methods such as UV light fracture detection became commonplace to ensure that only flawless O-rings reach end users, especially for high-stakes applications in aerospace, defense, and medical technology.
Design
Production Process
The manufacturing of O-rings typically employs either injection molding or compression molding. Injection molding is favored for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness, allowing manufacturers to produce large volumes of high-quality O-rings with precise tolerances. This process is ideal for industries requiring consistent, repeatable results—such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. Conversely, compression molding is suitable for smaller production runs or when working with specialty elastomers and custom shapes, though it requires more time and attention to detail.
Materials
Choosing the right O-ring material is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance in specific sealing environments. Manufacturers select from a broad spectrum of natural and synthetic elastomers, with the choice dictated by factors such as operating pressure, chemical compatibility, thermal requirements, and lubrication needs. When searching for the best O-ring material for your application, consider these core factors:
- Sealing pressure: Can the material withstand the internal or external pressure of the system?
- Chemical compatibility: Will it resist degradation when exposed to process fluids or chemicals?
- Temperature range: Is it suitable for the minimum and maximum operating temperatures?
- Lubrication: Does the seal require a lubricant, and is the material compatible with common lubricants?
Common O-ring materials include Teflon (PTFE), Viton (fluorocarbon), silicone, neoprene, nitrile (Buna-N), EPDM, perfluoroelastomer (FFKM), and fluorosilicone. Other materials such as polyamides, indium, melt-processible rubber, Sani fluor, clear plastics, and various metals are also available for specialized sealing requirements.
For aerospace and defense applications—where O-rings must withstand extreme temperatures, pressure cycling, and exposure to harsh chemicals—materials like EPDM, perfluoroelastomer, and fluorosilicone are often preferred. In the petrochemical and oil & gas industries, O-rings made from Viton, nitrile, perfluoroelastomer, and Teflon deliver proven resistance against aggressive fuels, solvents, and process chemicals.
Need help choosing the right O-ring material? Ask: What chemicals or pressures will my O-rings encounter? What are the temperature extremes in my process?
Design and Customization Considerations
Precision in O-ring design is critical for maximizing sealing performance and reliability. Manufacturers carefully evaluate:
- Material hardness (durometer) and durability
- Cross-section diameter and overall size
- Seal profile (standard round, square, rectangular, or custom shapes)
- Inner and outer diameters for correct fitment
- Metric vs. imperial (nonmetric) sizing standards
- Application-specific requirements such as FDA compliance, USP Class VI certification, or aerospace-grade tolerances
While round, donut-shaped O-rings are the industrial standard, custom profiles are available for unique or challenging sealing scenarios. Custom O-rings can be engineered for non-standard grooves, high-vacuum environments, or aggressive chemical exposure.
Searching for a custom O-ring solution? Ask: Can my O-ring supplier provide custom sizes or specialty materials for my application?
Features
Most O-ring seals feature a circular, disc-shaped cross-section. When installed in a groove between two mating surfaces, the O-ring is compressed—creating a tight, reliable seal that prevents gas or fluid leaks. The seal’s effectiveness increases with rising internal or external pressure. However, sealing integrity depends not just on deformation, but on the resilience of the O-ring material—its ability to recover its original shape after being compressed or stretched.
Key features of high-performance O-rings include:
- Excellent elasticity and recovery properties
- Resistance to abrasion, wear, and extrusion
- Stability across wide temperature and pressure ranges
- Chemical and solvent resistance
- Long service life and low maintenance requirements
- Suitability for both static and dynamic (moving) sealing applications
Curious about O-ring performance? Explore: How do different O-ring materials perform under pressure, temperature, or chemical exposure?
Types
Silicone O-Ring
Silicone O-rings are ideally suited for environments demanding resistance to rapid temperature fluctuations, extreme dryness, and intensive UV light exposure. Commonly used in medical devices, laboratory equipment, HVAC systems, and electronics, silicone offers outstanding flexibility and biocompatibility. Although more costly than other materials, silicone O-rings are prized for critical applications like earplugs, medical tubing, and high-temperature seals in food processing. They are also available in FDA-compliant grades for direct food or pharmaceutical contact.
EPDM O-Ring
EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) O-rings excel in sealing systems exposed to alcohols, acetone, water, steam, and polar solvents such as MEK (methyl ethyl ketone). They are widely used in potable water systems, HVAC, automotive brake systems, and appliances. However, EPDM is not compatible with petroleum oils, greases, or hydrocarbon fuels, making them unsuitable for those environments.
Neoprene O-Ring
Neoprene O-rings offer a balanced combination of strength, flexibility, and moderate resistance to heat, oil, and weathering. Frequently found in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, neoprene is effective in sealing refrigerants such as Freon. It is also used in general industrial applications that require resistance to ozone, sunlight, and moderate chemicals.
Viton O-Ring
Viton (fluorocarbon) O-rings provide exceptional chemical resistance and withstand extremely high temperatures—making them the material of choice for oil and gas refining, chemical processing, automotive fuel systems, and aerospace applications. Viton O-rings perform reliably in aggressive environments where other elastomers might fail, offering long-term sealing under harsh conditions.
Nitrile O-Ring
Nitrile (Buna-N) O-rings are the most widely used general-purpose sealing solution, valued for their excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons. They are cost-effective and suitable for a broad range of industrial applications, including automotive engines, fuel systems, hydraulic cylinders, and pneumatic controls. Nitrile O-rings are a go-to choice for manufacturers seeking a balance of affordability and performance.
Clear O-Ring
Clear O-rings are essential in medical, laboratory, and food and beverage processing environments where visual inspection and non-reactivity are paramount. Typically made from Teflon, polyurethane, or silicone, clear O-rings are available in ultra-clear or semi-clear grades. They are commonly used in IV tubing, peristaltic pumps, and sight glass assemblies, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory and hygiene standards.
Metal O-Ring
For extreme temperature and pressure applications where elastomeric O-rings would degrade or deform, metal O-rings offer superior strength and resistance. Manufactured from stainless steel, Inconel, or other metal alloys, these O-rings excel in high-vacuum, cryogenic, and corrosive chemical environments—such as semiconductor fabrication, aerospace, and nuclear industries. Metal O-rings are also used in static sealing applications requiring absolute leak-tightness.
Metric O-Ring
Metric O-rings are specified using the metric system (millimeters), which is standard in most regions outside the United States. Global equipment manufacturers and international projects often require metric O-rings to ensure compatibility and regulatory compliance.
O-Ring Cord
O-ring cord is a highly adaptable sealing solution, sold by the foot or meter. It enables users to cut custom lengths and join the ends to create made-to-measure O-rings for large-diameter or non-standard groove applications. O-ring cord is ideal for emergency repairs, prototyping, or low-volume production where off-the-shelf sizes are unavailable. Cord is available in a wide range of materials, including silicone, nitrile, Viton, and EPDM.
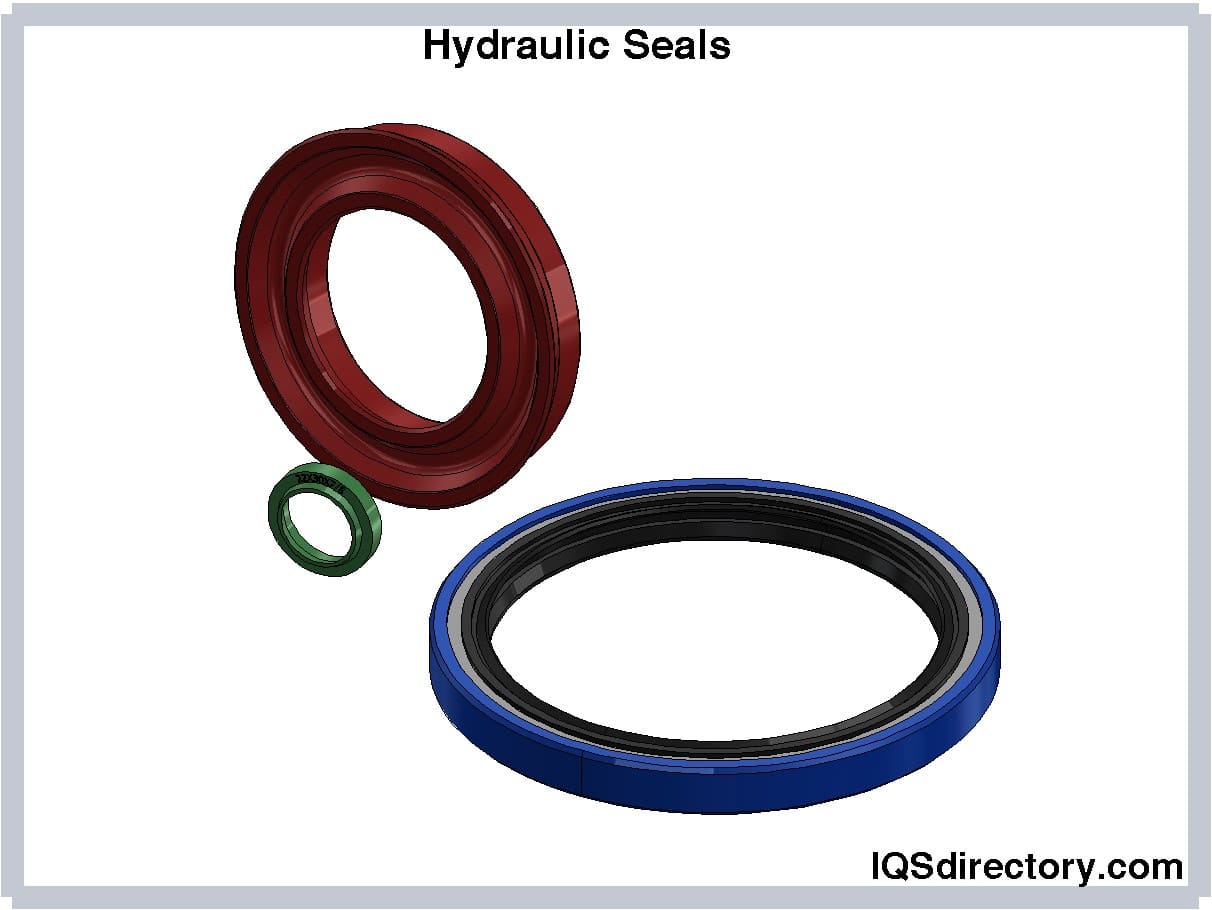
Oil Seal Gasket
An oil seal O-ring gasket serves several key functions in dynamic and static machinery:
- Prevents contaminants (dirt, dust, moisture) from entering sensitive equipment
- Keeps lubricants (oil, grease) securely contained within moving components
- Prevents cross-contamination between fluids, such as oil and water
Oil seal O-rings are integral to pumps, gearboxes, engines, and rotating shafts in automotive, industrial, and marine applications.
Advantages of O-Rings
O-rings deliver a compelling range of benefits over other types of seals and gaskets. Their main advantages include:
- Flexibility: O-rings can conform to uneven or irregular surfaces, ensuring a tight seal even when mating components aren’t perfectly aligned.
- Exceptional sealing capacity: They provide reliable, leak-proof performance under vacuum, low, and high-pressure conditions.
- Versatility: Available in a vast selection of materials and sizes, O-rings can be tailored for nearly any application or environment.
- Cost-effectiveness: Efficient manufacturing processes and readily available materials keep costs low, making O-rings an economical choice for both OEMs and MRO operations.
- Reusability: Many O-ring materials are durable enough for multiple installation cycles, reducing waste and saving on replacement costs.
- Ease of installation: O-rings are simple to install and remove, minimizing assembly time and labor costs.
Additionally, O-rings are capable of sealing across a broad temperature spectrum and can withstand pressures exceeding 100 bar (1,450 psi) in properly designed glands. They maintain sealing integrity under dynamic movement without causing excessive wear or requiring complex installation tools. O-rings’ simple geometry and adaptability allow them to be deployed in static (stationary) and dynamic (reciprocating, rotating) sealing applications.
Want to learn more about O-ring capabilities? Ask: Are O-rings suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature applications in my industry?
Accessories
Optimize your O-ring installations with essential accessories, including:
- Assembly greases and lubricants: Reduce installation friction and extend seal life
- O-ring kits: Pre-packaged assortments for maintenance teams or field repairs
- Extraction tools: Facilitate safe removal without damaging grooves
- Measuring cones and sizing tools: Ensure accurate selection and replacement
Not sure which accessories are right for your process? Explore: What O-ring tools or kits will streamline maintenance in my operation?
Installation
- Lightly apply a compatible lubricant to the O-ring unless your manufacturer specifies otherwise. Proper lubrication reduces friction and prevents twisting or tearing during installation.
- Cover all sharp edges on mating surfaces to prevent accidental cuts or nicks that could compromise the O-ring seal.
- Carefully place the O-ring between the components to be joined, ensuring it sits evenly in the groove.
- Stretch the O-ring evenly around the circumference, avoiding excessive force on one side.
- Do not exceed 50% stretch during installation to prevent permanent deformation or breakage.
- Check that the O-ring is not twisted or pinched in the gland or groove, as improper seating can lead to leaks or premature failure.
Need installation advice? Ask: What installation best practices can ensure optimal O-ring performance and longevity?
Proper Care for O-Rings
With proper maintenance, O-rings deliver long-term, reliable sealing performance. To maximize O-ring lifespan and effectiveness:
- Consider encapsulating O-rings with Teflon (PTFE-encapsulated O-rings) to protect against aggressive chemicals or abrasive process media.
- Use compatible lubricants to reduce friction and facilitate installation—but avoid lubricants containing the same base material as your O-ring, as this can cause erosion or swelling.
- Store spare O-rings in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight, ozone, and chemicals to prevent degradation.
- Maintain a set of replacement O-rings for critical equipment to minimize downtime during maintenance or unexpected failures.
Wondering how to maximize seal life? Ask: What storage, handling, and cleaning procedures will prolong the life of my O-rings?
Standards
O-ring standards are vital for ensuring product quality, consistency, and safety. Compliance with international and industry-specific standards reduces risk and streamlines procurement. Key standards include:
- ISO (International Standards Organization): Sets global benchmarks for O-ring dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications
- SAE International: Publishes aerospace standards (AS568, AS871, etc.) for O-rings used in aviation and defense
- ASTM: Specifies material properties and testing methods for elastomeric O-rings
- DIN/BS/JIS: Regional standards for metric O-ring sizes and performance
For regulated industries (such as food, pharma, medical, or aerospace), additional certifications (e.g., FDA, USP Class VI, NSF, or MIL-SPEC) may apply. Not sure which standards affect your project? Ask: What certifications or standards should my O-rings meet for compliance in my market?
Things to Consider
Choosing the right O-ring supplier ensures your project’s success and long-term reliability. To streamline your purchasing process and avoid unreliable vendors, start by preparing a detailed list of requirements and questions for potential manufacturers:
- What are the required pressure and temperature tolerances for my application?
- What O-ring sizes and shapes do I need?
- Can the manufacturer meet relevant industry standards and certifications?
- Are custom O-ring solutions available?
- What is the expected delivery timeline?
- How does the supplier handle quality control and traceability?
- What is my budget, and are there volume discounts?
- Can the supplier deliver to my location, and what are the shipping options?
Once you have your criteria, explore the trusted O-ring manufacturers listed above. Select several that align with your needs, reach out with your specifications, and compare their capabilities, responsiveness, and support. Look for partners with strong technical expertise, proven quality assurance processes, and a track record in your industry. After thorough evaluation, choose the manufacturer best suited to deliver high-quality, reliable O-ring solutions for your application.
Still have questions? Explore: How do I compare O-ring suppliers for quality, value, and technical support?
For more information, in-depth guides, or to request a quote, browse our directory of O-ring manufacturers and suppliers. Whether your focus is industrial sealing, medical device manufacturing, or specialized aerospace applications, you’ll find expert partners ready to help you select, customize, and source the ideal O-rings for your project’s success.
What are O-rings and where are they used?
O-rings are essential sealing devices used to control pneumatic, hydraulic, and vacuum flows in many industrial and commercial applications, including pump shafts, hydraulic pistons, gas caps, medical devices, automotive engines, food processing equipment, and more.
How are O-rings manufactured?
O-rings are typically produced using injection molding or compression molding. Injection molding is preferred for large-scale, high-precision production, while compression molding is used for small runs or when working with specialty elastomers and custom shapes.
What materials are commonly used to make O-rings?
Common O-ring materials include Teflon (PTFE), Viton (fluorocarbon), silicone, neoprene, nitrile (Buna-N), EPDM, perfluoroelastomer (FFKM), and fluorosilicone. Material selection depends on factors like pressure, chemical compatibility, and temperature requirements.
What are the main advantages of using O-rings?
O-rings are valued for their flexibility, exceptional sealing ability, versatility, cost-effectiveness, reusability, and ease of installation. They can perform across wide temperature and pressure ranges and are suitable for both static and dynamic applications.
How should O-rings be installed for best performance?
For optimal installation, lightly lubricate the O-ring, avoid sharp edges, place it evenly in the groove, don’t stretch it more than 50%, and ensure it’s not twisted or pinched. Proper installation prevents leaks and damage, maximizing performance and lifespan.
What are some important standards and certifications for O-rings?
Key O-ring standards include ISO for international specifications, SAE for aerospace and defense, ASTM for material properties, and regional standards like DIN, BS, and JIS. Regulated industries may require FDA, USP Class VI, or MIL-SPEC certifications.
How can I extend the lifespan of my O-rings?
To maximize the lifespan of O-rings, store them in a cool, dry, and dark environment, use compatible lubricants, encapsulate with Teflon for harsh conditions, and keep spare replacements available to minimize downtime during maintenance.




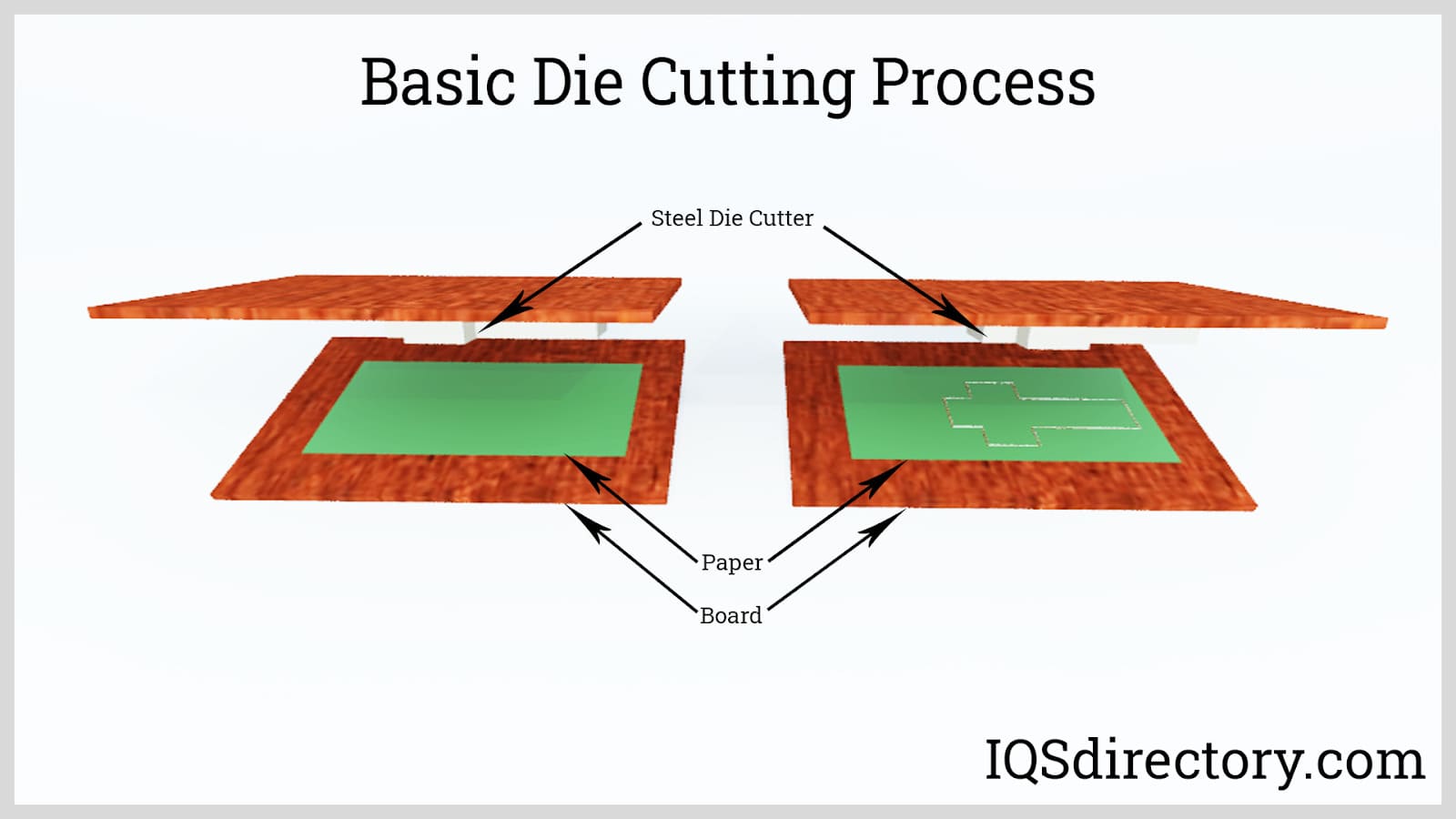
 Die Cutting
Die Cutting Foam Fab
Foam Fab Gaskets
Gaskets O-rings
O-rings Plastic Fabricators
Plastic Fabricators Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services